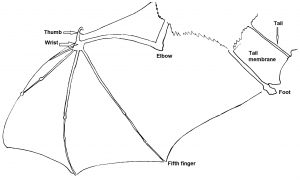
Bats are mammals. This means that they have fur covered bodies, they are warm blooded and give birth to live young. Mothers feed their newborn babies milk. Bats are the only mammals that can undertake true powered flight. A diagram of a bat’s wing is shown below. A bat’s wing is similar to a human hand except the thumb is small and claw-like, while the remaining digits (fingers) are long and there is skin stretched between them. There is a large area of wing membrane between the bat’s fifth finger and its body/leg.
Bats belong to the Order Chiroptera and there have been 1,466 species identified as of May 2024.
Many bat species, including all of the species found in Ireland, use sound to find their way around in the dark and to catch prey to eat. This is known as echolocation. Bats usually use very high pitched sounds beyond the range of human hearing (i.e. ultrasound) to echolocate.
In the tropics there is a wider variety of bat species. Fruit, insect, vertebrate and even blood consuming bats can be found in some warm tropical countries. Further north or south in cooler climates, bat faunas are usually less diverse and bats in northern Europe, including Ireland, are entirely insectivorous, i.e. they eat only insects.
In Europe, where 45 bat species have been recorded, there is just one species that eats fruit – the Egyptian fruit bat. Although it is found in parts of Africa and the middle east its European distribution is confined mainly to Cyprus and parts of Turkey.
In addition, the rare greater noctule bat found in Mediterranean countries regularly includes small birds in its diet.